One of the leading factors to quality issues with WebRTC is the distance between the user and your backend infrastructure. Even if there is a nearby server, there can be limiting factors such as the use of a VPN service by your customer or just bad routing rules, that get your user connected to the wrong server.
Here is how bad routing tend to look like in qualityRTC:
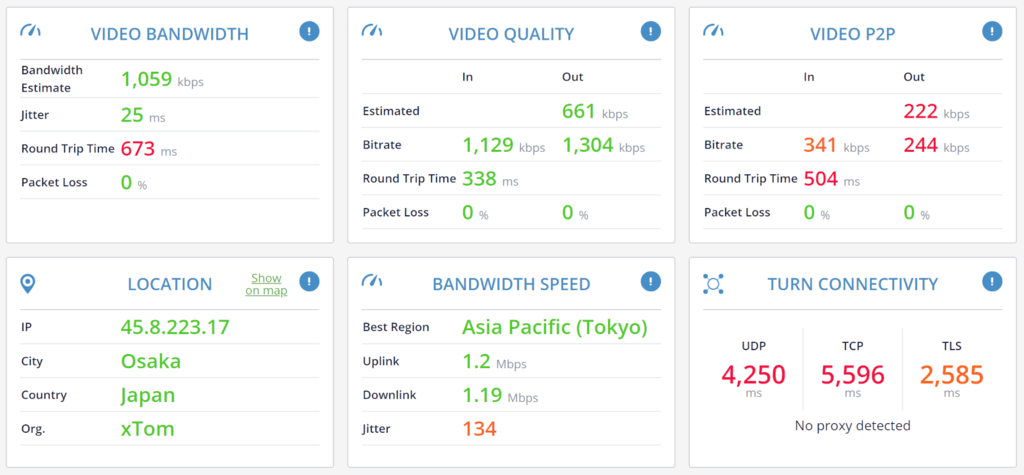
The WebRTC network test above was conducted in Israel, using a ProtonVPN client that was connected to a VPN server in Japan.
Here’s what we can see:
- VIDEO BANDWIDTH shows very high Round Trip Time (marked in red). This will result in poor quality and high latency for a video conversation
- VIDEO QUALITY and VIDEO P2P also show high Round Trip Time values
- VIDEO P2P shows low bitrate (it usually gets to 2Mbps)
- LOCATION shows the user is in Japan, while we know he is located elsewhere (in Israel)
- BANDWIDTH SPEED shows high jitter on uploading and downloading over HTTPS, with very poor connections of around 1.2Mbps
- TURN CONNECITIVTY shows slow connection times, but is still capable to connect UDP
What to do in such a case?
Ask your user if he is using a VPN. If he is, suggest removing it or configuring it in a way to allow WebRTC traffic to go unhindered for your service
